Dominic Hughes
Global Health Correspondent
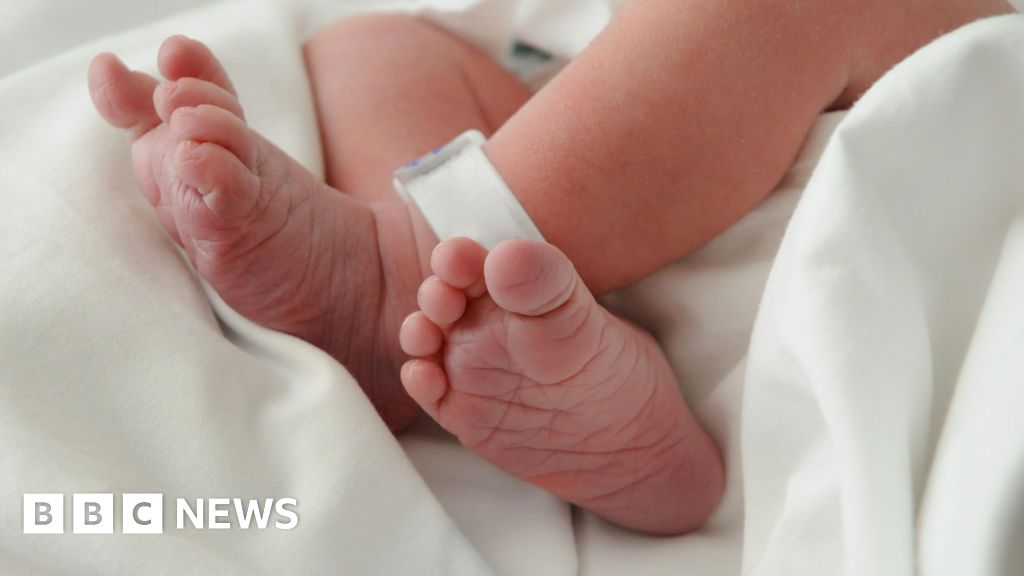
The first malaria treatment suitable for babies and very young children has been approved for use.
It's expected to be rolled out in African countries within weeks.
Until now there have been no approved malaria drugs specifically for babies.
Instead they have been treated with versions formulated for older children which presents a risk of overdose.
In 2023 - the year for which the most recent figures are available - malaria was linked to around 597,000 deaths.
Almost all of the deaths were in Africa, and around three quarters of them were children under five years old.
Malaria treatments for children do exist but until now, there was none specifically for the very youngest babies and small children, who weigh less than 4.5kg or around 10lb.
Instead they have been treated with drugs designed for older children.
But that presents risks, as doses for these older children may not be safe for babies, whose liver functions are still developing and whose bodies process medicines differently.
Experts say this has led to what is described as a "treatment gap".
Now a new medicine, developed by the drug company Novartis, has been approved by the Swiss authorities and is likely to be rolled out in regions and countries with the highest rates of malaria within weeks.
Novartis is planning to introduce it on a largely not-for-profit basis.
The company's chief executive, Vas Narasimhan, says this is an important moment.
"For more than three decades, we have stayed the course in the fight against malaria, working relentlessly to deliver scientific breakthroughs where they are needed most.
"Together with our partners, we are proud to have gone further to develop the first clinically proven malaria treatment for newborns and young babies, ensuring even the smallest and most vulnerable can finally receive the care they deserve."
The drug, known as Coartem Baby or Riamet Baby in some countries, was developed by Novartis in collaboration with the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV), a Swiss-based not-for-profit organisation initially backed by the British, Swiss and Dutch Governments, as well as the World Bank and the Rockefeller Foundation.
Eight African nations also took part in the assessment and trials of the drug and they are expected to be among the first to access it.
Martin Fitchet, CEO of MMV, says this is another important step on the road towards ending the huge toll taken by malaria.
"Malaria is one of the world's deadliest diseases, particularly among children. But with the right resources and focus, it can be eliminated.
"The approval of Coartem Baby provides a necessary medicine with an optimised dose to treat an otherwise neglected group of patients and offers a valuable addition to the antimalarial toolbox."
Dr Marvelle Brown, associate professor at the University of Hertfordshire's School of Health, Medicine and Life Sciences, says this should be seen as a major breakthrough in saving the lives of babies and young children.
"The death rate for malarial infections, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa is extremely high - over 76% of deaths occur in children under five years old.
"Increase in death from malaria is further compounded in babies born with sickle cell disease, primarily due to a weak immune system.
"From a public health perspective, Novartis making this not-for-profit can help with reducing inequality in access to healthcare."

 German (DE)
German (DE)  English (US)
English (US)  Spanish (ES)
Spanish (ES)  French (FR)
French (FR)  Hindi (IN)
Hindi (IN)  Italian (IT)
Italian (IT)  Russian (RU)
Russian (RU)  3 weeks ago
3 weeks ago























Comments